Refer to the Diagram. The Monopolistically Competitive Firm Shown
If all monopolistically competitive firms in the industry have profit circumstances similar to the firm shown above. 4 units at an economic profit of 3175.

Solved Refer To The Diagram For A Monopolistically Chegg Com
521 Monopolistic Competition in the Short and Long Runs.
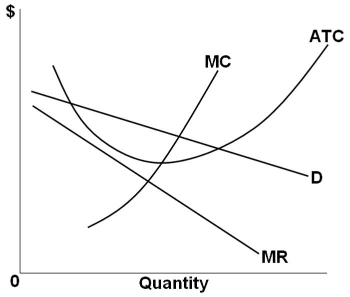
. A monopolistically competitive firm perceives a demand for its goods that is an intermediate case between monopoly and competition. Not be maximising its profit. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium.
In contrast the demand curve as faced by a. Long-run equilibrium is shown by diagram b only. Will realize allocative efficiency at its profit-maximizing output.
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. 6 In long-run equilibrium production for the firm shown in the diagram above is. New firms will enter the industry.
This firm will realize an economic. The monopolistically competitive firm shown Multiple Choice is in long-run equilibrium. Long-run equilibrium is shown by diagram b only.
Diagram c only. MR Quantity Refer to the diagram. New firms will enter the industry.
Be losing market share to other firms in the market. 1 Making Economics Decisions 2 Estimating Engineering Costs And Benefits 3 Interest And Equivalence 4 Equivalence For Repeated Cash Flows 5 Present Worth Analysis 6 Annual Cash Flow Analysis 7 Rate Or Return Analysis 7A Difficulties In Solving For An Interest. If the market price for the firms product is 32 the competitive firm.
The monopolistically competitive firm decides on its profit-maximizing quantity and price similar to the way that a monopolist does. Business Economics QA Library Refer to the diagrams which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. As shown in Figure 84d this occurs when P ATC and MR MC.
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. A monopolistically competitive firm faces a demand for its goods that is between monopoly and perfect competition. The profit-maximizing ouput for this firm will be.
Ο is realizing an economic profit. Short-run equilibrium entailing economic loss is shown by. In short-run equilibrium the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price.
Refer to the diagram in short-run equilibrium the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price. First at its optimum output the firm charges a price that exceeds marginal costs. This firm will realize an economic.
Refer to the diagrams which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. No firms will enter the industry. The monopolistically competitive firm in the short run.
Figure 1 offers a reminder that the demand curve as faced by a perfectly competitive firm is perfectly elastic or flat because the perfectly competitive firm can sell any quantity it wishes at the prevailing market price. Long-run equilibrium is shown by diagram bonly. Refer to Graph 17-1.
Cannot operate at a loss. Zero units at a loss of 100. 4 units at a loss of 109.
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. Refer to the above diagram. If all monopolistically competitive firms in the industry have profit circumstances similar to the firm shown above A.
ATC MC MC ATC D 0 MR Quantity a 0 MR Quantity b ATC MC D 0 MR Quantity c Question. Refer to the diagram. If all monopolistically competitive firms in the industry have profit circumstances similar to the firm shown above.
Multiple Choice Ο is in long-run equilibrium. Refer to the diagrams which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. If the market price for the firms product is 12 the competitive firm will produce.
A monopoly exists when a person or entity is the exclusive supplier of a good or service in a market. Be operating at excess capacity D. The firms profit-maximizing price will be.
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. Is realizing an economic profit. All firms will exit the industry.
Refer to the above diagrams which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Refer to the above diagram in which S is the market supply curve and S1 is a supply curve comprising all. The demand curve of a monopolistically competitive firm is downward sloping indicating that the firm has a degree of market power.
In short-run equilibrium the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price. Some firms will exit the industry. Be minimising its losses B.
Refer to the above data. None of these diagrams. Markets that have monopolistic competition are inefficient for two reasons.
Refer to Graph 17-1. Ο will realize allocativ will realize allocative efficiency at its profit-maximizing output. Is realizing an economic profit.
Monopolistic competition is different from a monopoly. If a monopolistically competitive firm is earning positive economic profits entry will occur until economic profits are equal to zero. Figure 84a offers a reminder that the demand curve as faced by a perfectly competitive firm is perfectly elastic or flat because the perfectly competitive firm can sell any quantity it wishes at the prevailing market price.
The following TWO questions refer to the. Refer to the above data. As long as P ATC firms will continue to enter the market and demand will continue to shift inward.
8 units at a loss of 4880. If a firm in a monopolistically competitive market was producing the level of output depicted as Qd in panel d it would. This firm will realize an economic.
Is in long-run equilibrium. The monopolistically competitive firm shown.

Module 06 B Practice Quiz Flashcards Quizlet

Solved 1 Refer To The Diagram Above The Monopolistically Chegg Com

No comments for "Refer to the Diagram. The Monopolistically Competitive Firm Shown"
Post a Comment